Treating Tendinitis in Hopkinsville and Preventing Recurrence

Tendinitis occurs when a tendon is inflamed. Tendons play a vital role in the ability of the muscles to move bones. Often, tendinitis develops in the shoulder, wrist, elbow, bicep, ankle, knee, calf, and thumb. The pain happens near a joint, so tendinitis is often mistaken as arthritis. Athletes and those who are at least 40 years old are prone to having this condition.
Tendinitis usually occurs because of repetitive movements or sports injuries. Also, it can be due to bad walking habits or posture, an infection, soft tissue stress, some medications, metabolic conditions like diabetes, and some kinds of arthritis. Thankfully, Hopkinsville tendinitis treatments are available to help relieve the symptoms of the condition.
Symptoms of Tendinitis
Tendinitis results in pain, tenderness, and inflammation in the affected area around a joint like the tendons, muscles, and ligaments. Some kinds can develop suddenly and last for several days or weeks. Those who have this condition can experience more serious pain whenever they move and the pain may get better when they rest or get treatment. Symptoms of tendinitis can occur again in the same body area.
Treatment for Tendinitis
Over time, tendinitis may disappear. If not, a sufferer should get treatment for pain and inflammation. Also, their treatment includes those to preserve their mobility. Patients with serious symptoms may require specialized treatment from a physical therapist, rheumatologist, or orthopedic surgeon. Proper treatment for tendinitis is important to avoid permanent damage to the joint or disability. The following are common treatment options for this condition:
- Rest, ice, compression, elevation (RICE). A lot of soft tissue conditions result from muscle overuse. Thus, the initial treatment for tendinitis may include RICE.
- Therapy. Physical therapy includes hot and cold treatments, manual therapy, ultrasound, water and laser therapy, a personalized exercise program, and more. Also, occupational therapy can include the use of assistive devices, making changes to work habits, and modifying everyday activities.
- Medications. OTC and prescription medicines include pain relievers or NSAIDs. Depending on the seriousness of the symptoms, a doctor may prescribe a stronger NSAID as a pain reliever.
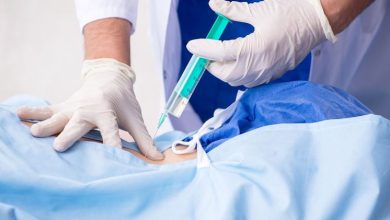
- Corticosteroid injections. Doctors inject these drugs directly into the affected joint.
- Surgery. A person with tendinitis may need surgery if their tendon ruptures or when they have tendon lesions.
Preventing Recurrence
Since tendinitis often results from overuse, a person can prevent recurrence by avoiding or changing activities that cause the condition. Their occupational or physical therapist can offer suggestions on changing their activities. Also, exercises to improve range of motion may help minimize stiffness and improve flexibility.