Peripheral Artery Disease: Causes, Risk Factors, and Potential Treatments
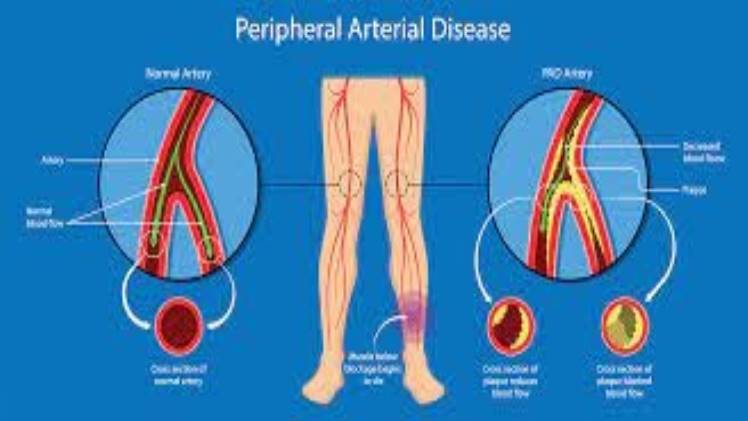
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) is a condition where the blood vessels narrow and limit blood flow to various organs. It often affects the limbs, where the blood pressure is higher than the rest of the body. You can manage PAD Tomball with lifestyle changes, medication, or minimally-invasive treatments. Here are the PAD causes, risk factors, and potential therapeutic interventions.
What causes PAD?
PAD occurs due to a plaque buildup in the arteries, limiting blood flow often in your limbs. Plaque consists of cholesterol and other compounds in your body.
Plaque tends to stick on the smooth wall of the arteries. The deposit narrows the arteries, which limits the flow of oxygen and nutrients to the different organs. The lack of oxygen and nutrients can kill healthy tissues.
In rare cases, other factors may lead to Peripheral Artery disease. They include:
- Blood vessel inflammation and infections: A blood vessel inflammation can trigger or encourage PAD’s disease progression. Inflammation could be due to infections or an autoimmune condition.
- Blood vessel defects: Some blood vessel defects are present from childbirth. They may narrow the vessel and restrict blood flow.
- Trauma or injury: Your arteries may become damaged after an impact on specific areas of the body. The trauma may deform blood vessels and cause PAD to develop.
- Treatments utilizing radiation therapy: Research has also identified radiation therapy for cancer treatments as a factor for peripheral artery disease. Radiation may cause injuries to the blood vessels making the patient susceptible to PAD. The risk varies depending on the patient’s diet and level of physical activity.
PAD risk factors
Several factors may increase your risk of PAD. You are more likely to develop the condition if your family has a medical history of PAD.
People over 65 have a higher risk of PAD. Older adults with the condition are also susceptible to cardiovascular diseases.
Obesity and inactivity can also raise your risk of developing peripheral arterial disease. Exercise strengthens leg muscles and promotes the functional capacity of blood vessels.
You may be at high risk of PAD if you smoke or are actively exposed to cigarette smoke. The nicotine in tobacco damages blood vessels. It affects the functional capacity of arteries, encouraging the progression of PAD.
PAD complications and potential therapeutic interventions
If untreated, PAD may lead to severe complications. PAD may cause tissue in your limbs to die, prompting an amputation. At that stage, patients have wounds that do not respond to treatment.
The principal cause of PAD is the accumulation of plaque in the arteries. A spike in blood pressure also increases your risk of heart disease and stroke.
You can manage mild to moderate PAD cases with dietary adjustments and lifestyle changes. Your provider may recommend exercise to boost vascular function.
Prescription medication is sometimes necessary to address co-occurring conditions like hypertension. It can also slow the accumulation of plaque.
In severe cases, balloon angioplasty and stenting procedures are necessary to restore blood flow. The process unclogs the artery to allow nutrients to reach the organs.
To explore minimally-invasive PAD interventions, call Northwest Houston Heart Center to book your consultation today.